
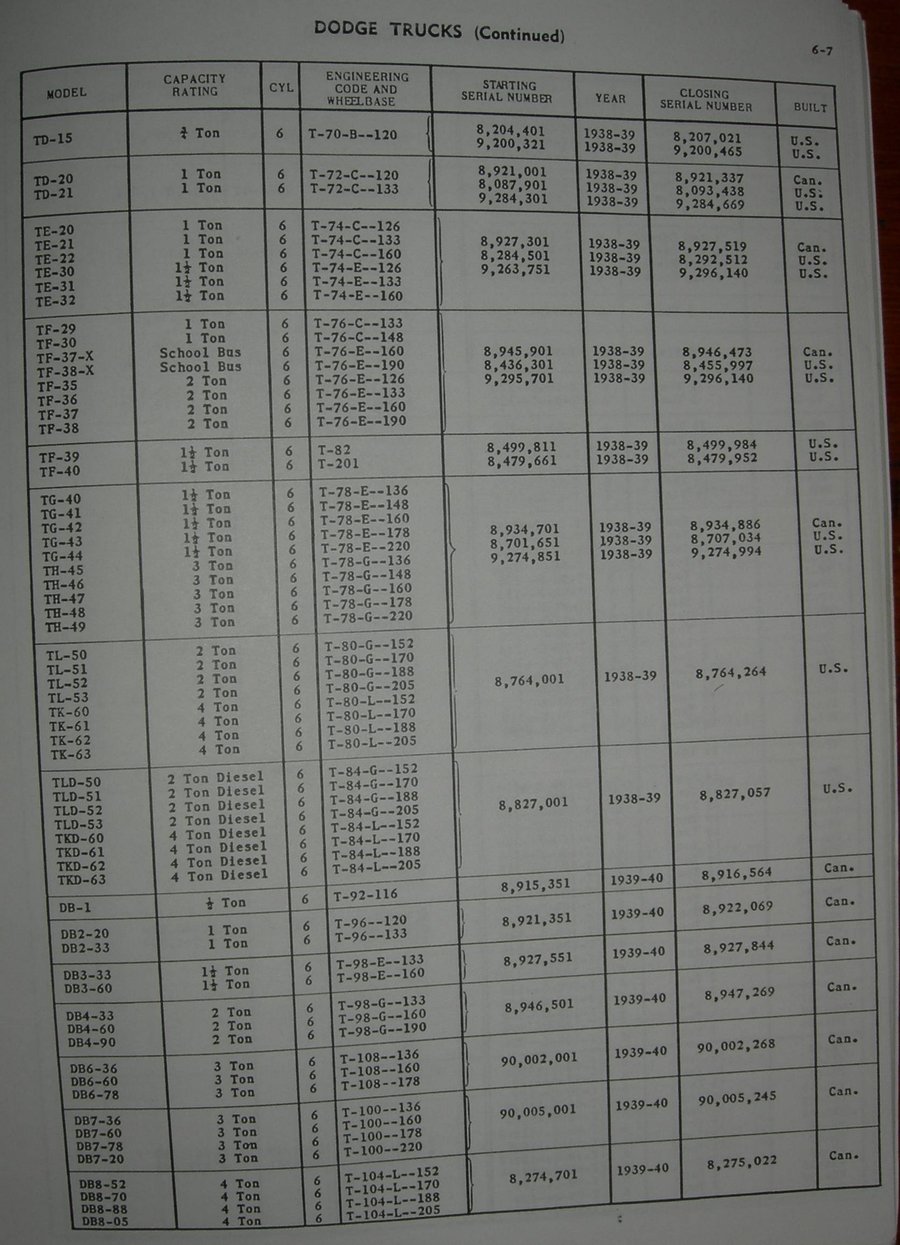
DATAGRAPH SERIAL NUMBER SERIES
In 1964, IBM introduced its System/360 series which used microcode to allow a single expansive instruction set architecture (ISA) to run across a wide variety of machines by implementing more or less instructions in hardware depending on the need. Providing these different instructions allowed the programmer to select the instruction that took up the least possible room in memory, reducing the program's needs and leaving more room for data.Īctually making these instructions work required circuitry in the CPU, which was a significant limitation in early designs and required designers to select just those instructions that were really needed. For instance, the add A to B to produce C instruction would be provided in many different forms that would gather A and B from different places main memory, indexes, or registers. In the 1960s memory was relatively expensive, and CPU designers produced instruction sets that densely encoded instructions and data in order to better utilize this resource. Over time, the relative performance and cost of the different steps have changed dramatically, resulting in several major shifts in ISA design. Most instructions require several internal steps to complete an operation. ( June 2018) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message)Īlmost all computer programs consist of a series of instructions that convert data from one form to another. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. This article possibly contains original research.

Major development of the EDGE concept had been led by the University of Texas at Austin under DARPA's Polymorphous Computing Architectures program, with the stated goal of producing a single-chip CPU design with 1 TFLOPS performance by 2012, which has yet to be realized as of 2018. Parallelism of modern CPU designs generally starts to plateau at about eight internal units and from one to four "cores", EDGE designs intend to support hundreds of internal units and offer processing speeds hundreds of times greater than existing designs. Hyperblocks are designed to be able to easily run in parallel. EDGE combines many individual instructions into a larger group known as a "hyperblock". For other uses of the acronym EDGE, see Edge (disambiguation).Įxplicit data graph execution, or EDGE, is a type of instruction set architecture (ISA) which intends to improve computing performance compared to common processors like the Intel x86 line. For the women's educational support organization, see EDGE Foundation. For the digital mobile phone technology, see Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution. This article is about the instruction set architecture type.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
